January 2025 Project Update
We’re kicking off 2025 with exciting progress on Athena! This month, we launched the first public devnet, implemented the PROXY method, and introduced new token-related smart contracts. Let’s dive into the details.
First Public Devnet Released
We’re thrilled to announce the release of Athena’s first public devnet! Developers can now test, experiment, and implement smart contracts on Athena. This is a Proof of Concept (PoC) where AthenaVM replaces the Spacemesh VM on L1. However, in the final design, AthenaVM will work alongside the genesis VM—more details on that will come in future updates.
If you’re interested in testing it out, we welcome you to deploy your own contracts and explore its capabilities. Your feedback will be invaluable in refining the system!
To join the network, please follow the guide located here.
PROXY Method Implemented
A major milestone this month was the implementation of the PROXY method, now integrated into the single-signature wallet.
This method enables one contract to call another while handling transaction fees and
optionally transferring funds to the target contract.
Importantly, the transaction is always signed by the principal wallet, ensuring clear authorization.
This feature has already proven useful in implementing token-related smart contracts—see the next section for details!
Token Mint and Token Wallet Contracts
To demonstrate Athena’s capabilities, we implemented two new example smart contracts: a Token Mint and a Token Wallet. These contracts allow users to create and exchange custom tokens.
- Token Mint Contract: Governs the creation of a specific token. Every instance of a mint contract defines a new, unique token. Users exchange SMH for these tokens, which are then stored in a token wallet.
- Token Wallet Contract: Manages token balances and enables transfers between accounts. A single wallet can hold multiple tokens, each identified by the address of the mint account that created them.
We recorded a video explaining how these contracts work:
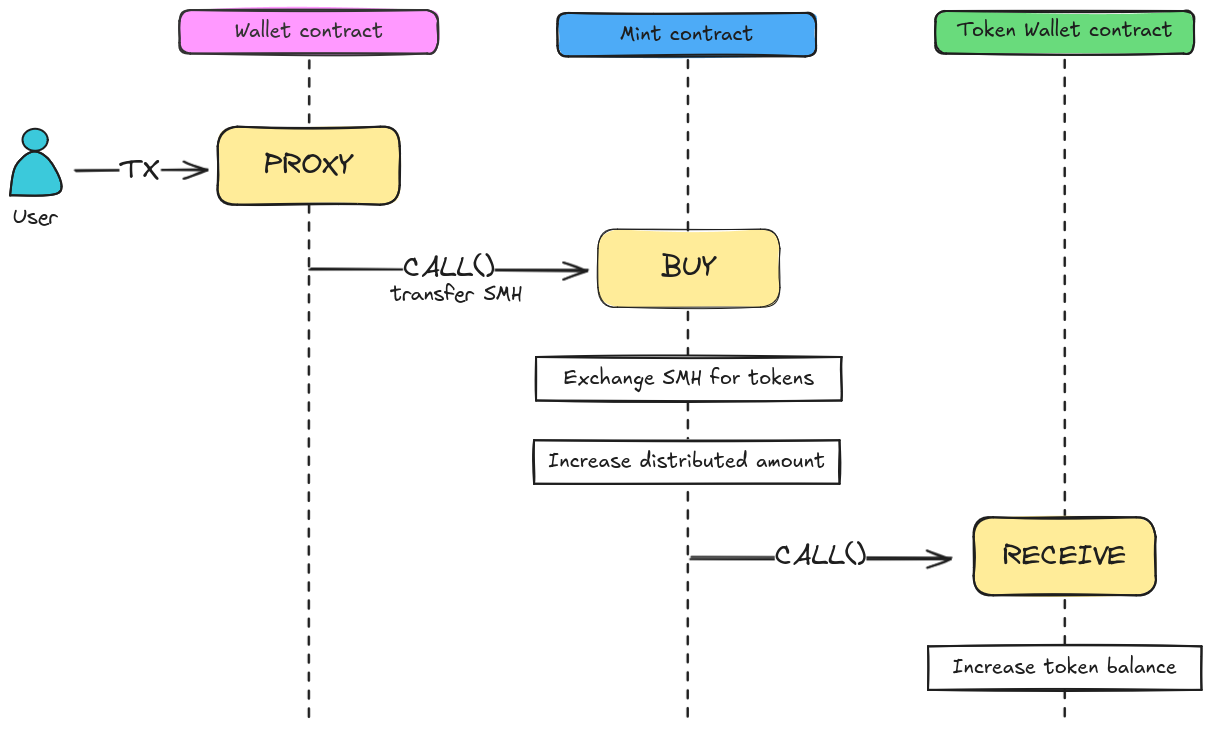
How Users Exchange SMH for Tokens
The process of exchanging SMH for a token involves three contracts working together:
- The user creates a transaction invoking the
PROXYmethod on a wallet contract that holds SMH. ThePROXYmethod ensures that the wallet pays all transaction fees and forwards a method call to another contract while transferring SMH to the called account. - The recipient contract in this case is the mint contract, where the user is purchasing tokens.
The
PROXYmethod calls theBUYmethod in the mint contract, transferring SMH funds to it. - The mint contract verifies the received SMH, checks the available token supply,
and transfers the appropriate number of tokens to the token wallet contract by calling its
RECEIVEmethod. - The token wallet contract, rather than the mint, is responsible for maintaining token balances.
When the
RECEIVEmethod is called, the wallet contract increases its balance by the specified token amount.
Below is a diagram illustrating how one can purchase tokens using these contracts:
The code of these contracts is available on GitHub:
MINT
and
WALLET.
Looking Ahead
- We will continue refining the devnet and addressing early feedback from developers.
- We are working hard on finalizing the AthenaVM architecture and moving from the PoC to a final solution.
Contributing
Athena is being built fully in the open, and the codebase is fully open source and permissively licensed.
If you’re interested in contributing, take a look at the list of issues tagged Help Wanted and Good First Issue on GitHub.
Thank you for your continued support and interest in Athena. As always, we welcome your feedback and encourage you to experiment with the devnet. Please to follow the project on GitHub and X, and to join the conversation in the #athena-vm channel on our Discord to stay up to date with our developments.
Stay tuned for more updates next month!